Titanium Engine
Github (Engine Source) Github (Engine Examples)
Titanium Engine is a Vulkan based game engine that is still in development process for researching the effects of AI on game development.
Introduction
The Titanium Engine leverages Vulkan to support the latest graphics standards and ensure multi-OS compatibility, enhancing its capabilities for advanced AI research. This decision aligns with the engine’s goal of delivering cutting-edge performance and flexibility.
At the heart of the system, Vulkan operations are managed by the Vulkan Manager, which serves as the primary interface for interacting with the Vulkan API. The Vulkan Manager is closely integrated with the Graphics Manager, which oversees various Render Systems tailored to different shaders, ensuring optimal rendering workflows.
To facilitate mathematical computations essential for graphics programming, the Titanium Engine incorporates GLM (OpenGL Mathematics). This library provides robust tools for tasks such as matrix transformations, vector operations, and quaternion calculations, making it a critical component in enabling advanced computer graphics functionality within the Vulkan-powered framework.
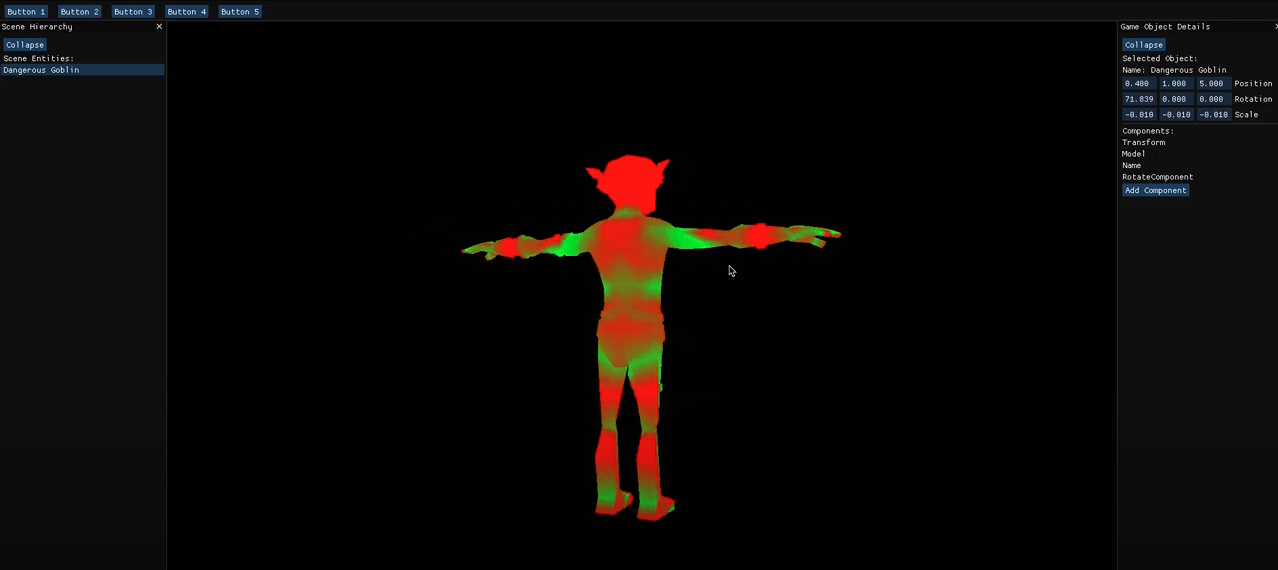

Engine Structure
The Titanium Engine is designed around Entity Component System (ECS) principles, ensuring a fully data-oriented approach, even for the engine’s core code. The Entity Manager serves as the backbone for managing all in-game entities. It supports efficient querying for entity operations and employs archetypes to store entities in batches, ensuring optimal memory usage and performance. To maintain high efficiency, the ECS system leverages contiguous memory alignment and implements an effective strategy for updating entities, maximizing both speed and scalability.
AI components are seamlessly integrated into the ECS framework. However, due to the computationally intensive nature of certain AI systems, they are not guaranteed to execute every frame or even every second. Instead, the Entity Manager dynamically calculates optimized intervals for AI execution, redistributing resources to other game modules and maintaining performance balance.
AI Assistant Integration
Titanium Engine also boasts a powerful AI Assistant, integrated via an Assistant Manager and Qt for seamless data retrieval from the engine. The Assistant operates as a standalone application, built using Next.js, and employs both AI Agents and a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approach to handle user queries effectively. This modular design allows for the underlying Large Language Model (LLM) to be swapped out at any time, ensuring adaptability for future developments.
Native AI Agents
The engine also features native AI agents, enabling dynamic NPC interactions and runtime AI computations. While the AI Assistant is designed to enhance the development process, the native agents ensure seamless integration of large language models (LLMs) within the runtime application.
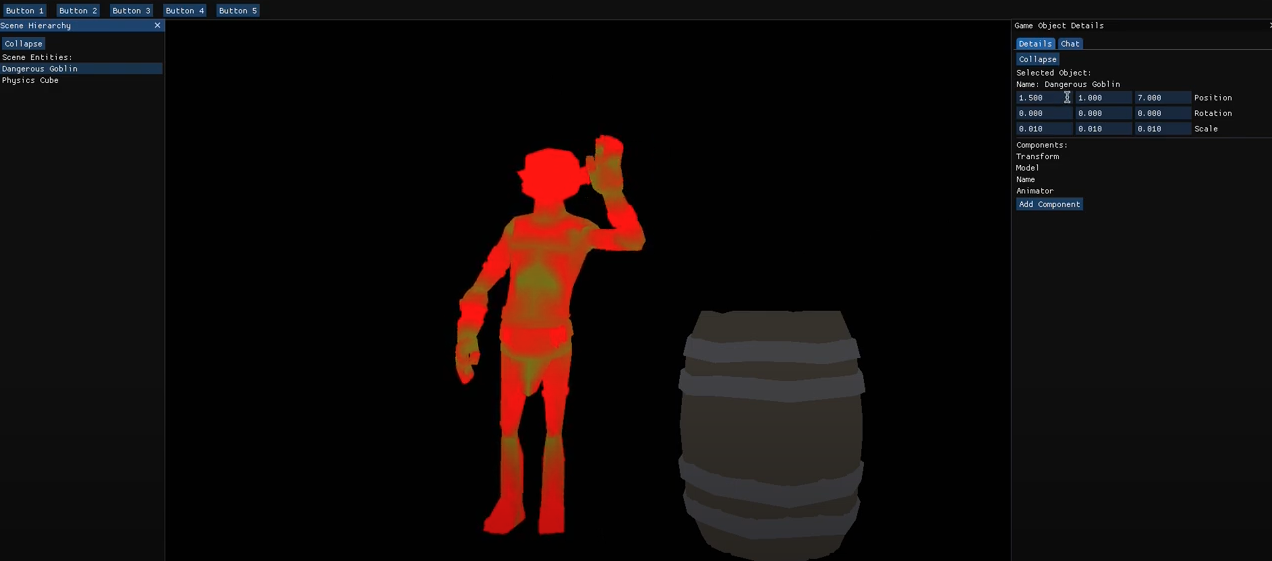

Visual Scripting
The engine includes robust Visual Scripting capabilities, accessible through the AI Assistant. Visual Scripting allows developers to construct logic by connecting nodes, which is then compiled into optimized C++ code for runtime efficiency. This feature empowers developers to create complex systems easily, and its integration with the AI Assistant unlocks additional possibilities, such as using state machines generated in the editor as input for LLMs to produce highly refined results.
LLM Integration
The Titanium Engine Assistant seamlessly integrates support for both Ollama models and the ChatGPT API. Notably, it leverages advanced AI agents and a sophisticated chain-of-thought approach to efficiently tackle a wide range of tasks. These include, but are not limited to, level design generation, code development, state machine creation, and debugging engine logs.
ML Models Integration
TensorFlow is utilized within the engine for training specialized machine learning models, with the AI Manager seamlessly connected to a Python TensorFlow module that handles the creation and training of models for NPCs, bosses, and various in-game systems. These use case-specific ML models excel in targeted scenarios, offering optimized performance and efficiency when compared to general-purpose LLMs, especially in situations where text generation or broad informational capabilities are not required. This tailored approach ensures that the AI systems are highly focused on gameplay needs, delivering precise and computationally efficient solutions for specific game mechanics.